Glossary
 Lukas
Zmejevskis
Lukas
Zmejevskis
In our blog and software help we often use terminology that might not be clear for everyone. Thus we decided to create our own glossary of most common terms used in the context of photogrammetry.
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry – science and technology used to obtain information from photographs. Digital 3D Photogrammetry is mainly used to create 3D models of scenes and objects photographed with a digital camera. Photogrammetry has limitless possibilities and applications in science and art.
A Drone
Drone – also known as an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle or UAV – is a flying device with no pilot on board. Drones can be of various sizes and designs made for the military, recreational, surveying, inspection, creative, and other purposes.
Payload
Payload – a device or a cluster of devices carried by an aerial vehicle in addition to all crucial components needed for flight. The most common payload for drones is usually the cameras.
Camera
Camera – a device used for capturing photographs. Cameras can be standalone and integrated into a larger device, such as a drone or a smartphone. Standalone cameras usually consist of a camera body containing the imaging sensor and a lens. A battery and memory card are essential components for camera operation.
Camera Lens
Camera Lens – the optical part of the camera used to focus light on the camera sensor. Lenses can be integrated into a camera or interchangeable. Camera lenses can be of varying focal length (zoom) or fixed focal length (prime). Camera lenses can contain autofocus and image stabilization alongside other additional features.
Image Overlap
Image Overlap – a percentage value of adjacent images covering the same area. Image overlap of the same object with different camera locations is essential for photogrammetry algorithms. It is what enables the 3D reconstruction of scenes and objects.
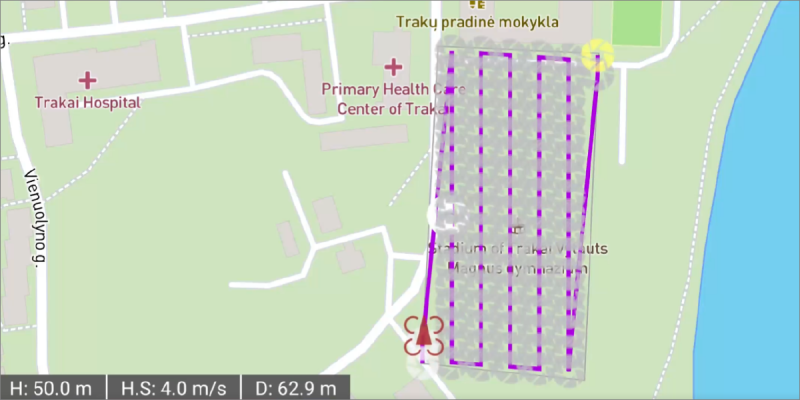
Flight Plan
Flight Plan – a predetermined path of an aerial vehicle with other variables if necessary. A drone flight plan for photogrammetry usually consists of the path and photo locations. Flight plans enable users to create consistent and efficient flights for photogrammetry purposes.
Image File Format
Image File Format – a digital container used to store a digital photograph or an image. Image format can be determined by the file extension – letters following the file name, e.g. .jpg. Most popular image formats include .jpg; .png; .tif; .tiff; .dng; and others.
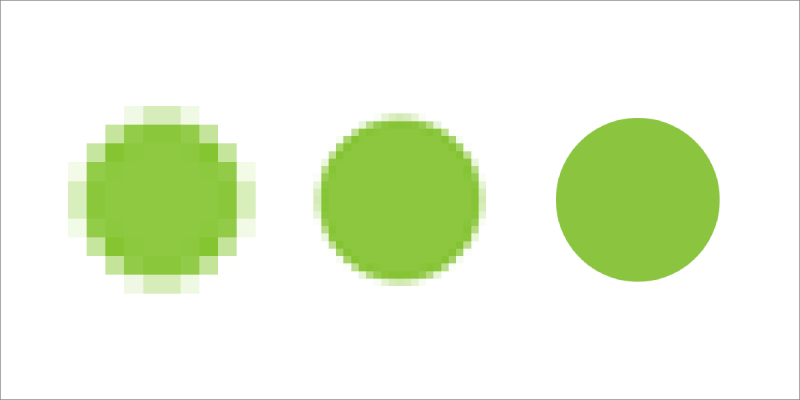
Image Resolution
Image Resolution – the ability of an image to hold detail. Many factors can influence image resolution. Resolution also commonly refers to the image dimensions in pixels. The more pixels, the more detail can be extracted from the image. A 12-megapixel photo will have less resolution than a 50-megapixel image with other factors being equal.
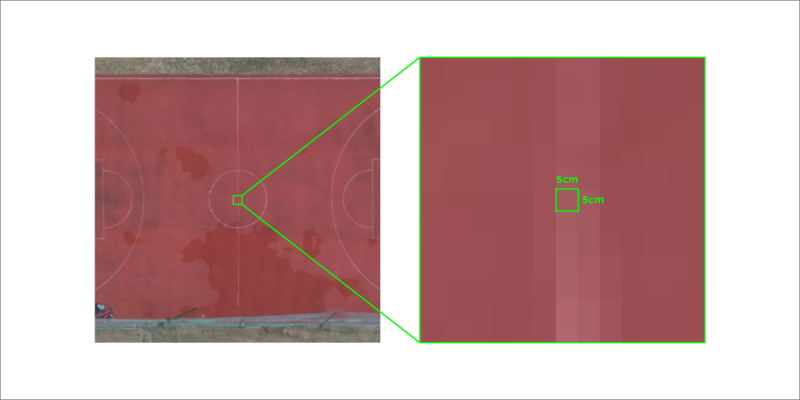
Ground Sampling Distance
Ground Sampling Distance or GSD – a numerical value that represents the size of a single-pixel in the real world once a photo is taken. An example: 5cm/px would mean that a single pixel represents a 5 centimeter square in the photographed scene. GSD depends on the distance between the camera and the subject, camera sensor size, resolution, and lens focal length. The smaller the GSD number, the more detail we expect to see in the scene.
Photo Exposure
Photo Exposure – the amount of light gathered for a photo. Exposure is a sum of a few variables that determine how bright a photograph will be. Those variables are the aperture of the lens and the shutter speed. Additionally, the camera sensor sensitivity is considered an exposure variable as well. Photos can be underexposed – too dark or overexposed – too bright.
Image Processing
Image Processing also known as Post-Processing – is a process when images are processed to a particular goal. For example, Photogrammetric Processing would mean running photogrammetry algorithms and getting a 3D project.
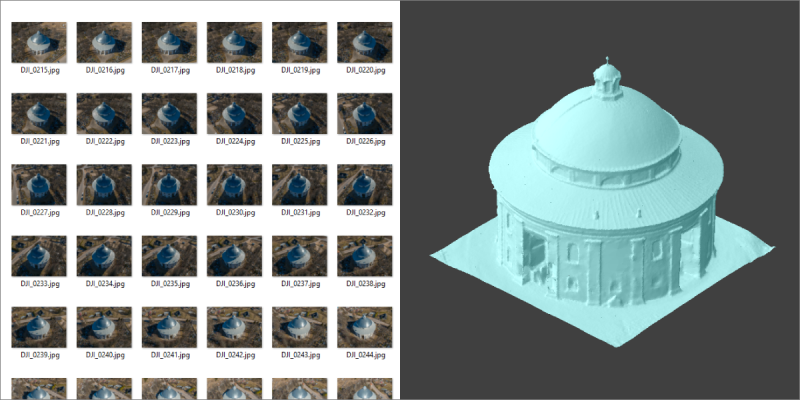
3D Reconstruction
3D reconstruction – the initial phase of the digital 3D photogrammetry process. An initial sparse point cloud and camera positions are generated during this process.
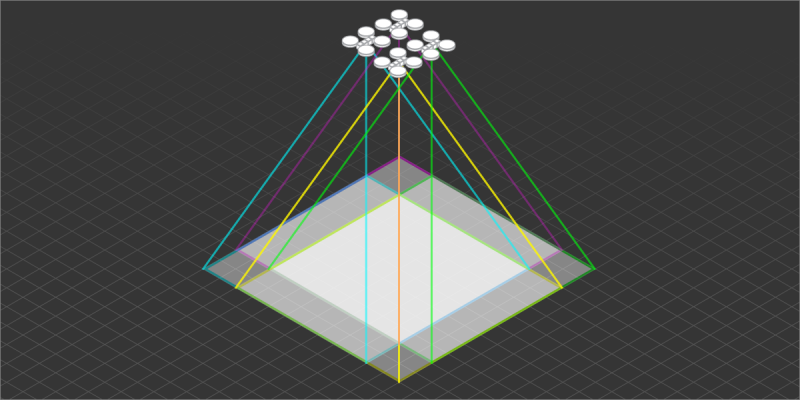
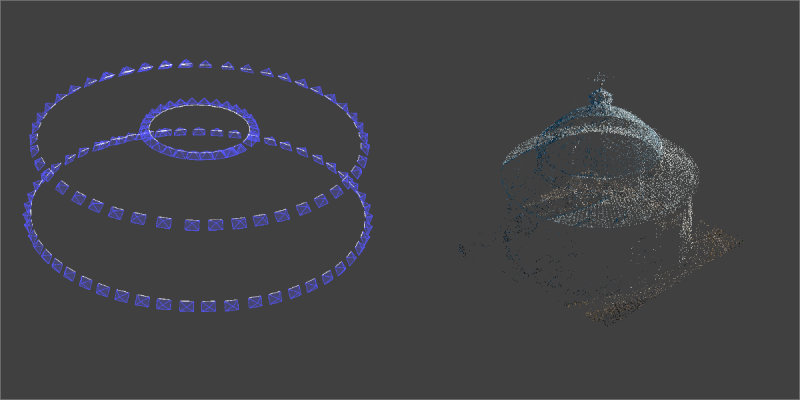
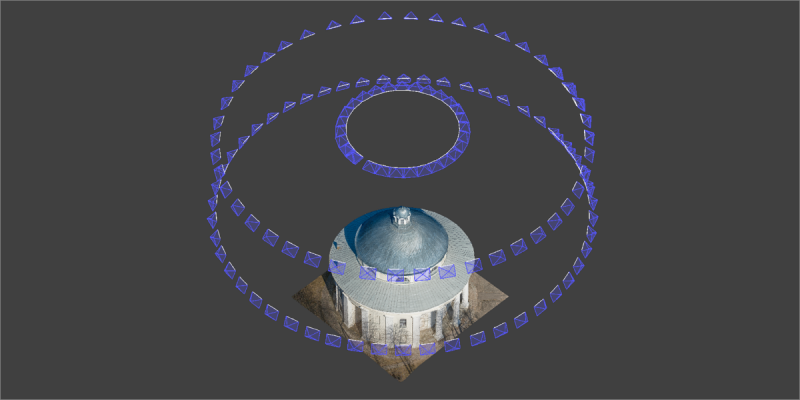
Camera Positions
Camera Positions – locations where the photos were taken during the photogrammetric scan. Camera positions are computed during the 3D reconstruction process, but can be seen prior to computation if the input photos contain referencing data.
Sparse Point Cloud
Sparse Point Cloud – a 3d point cloud obtained after the 3D reconstruction phase is complete. Also known as Tie Points, 3D Structure. Sparse point clouds are usually not dense enough to recognize the scene or produce other 3D layers.
Dense Point Cloud
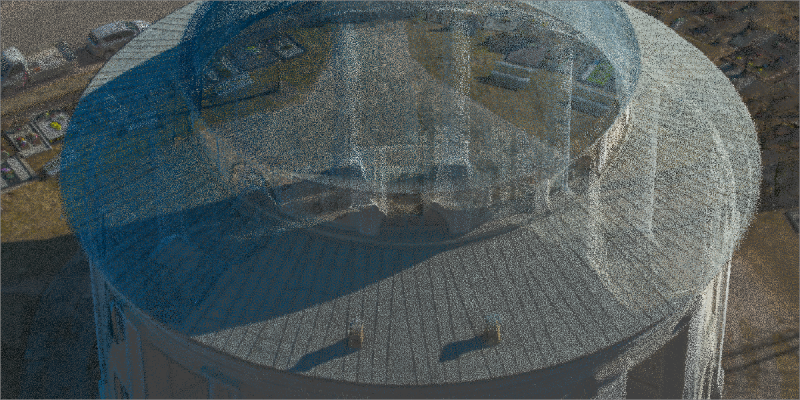
Dense Point Cloud – a cluster of 3D points in a 3D space. Point clouds can be generated using laser scanning or with the help of photogrammetry. Dense point clouds usually are the input data for 3D meshes and other subsequent 3D project layers.
3D Mesh
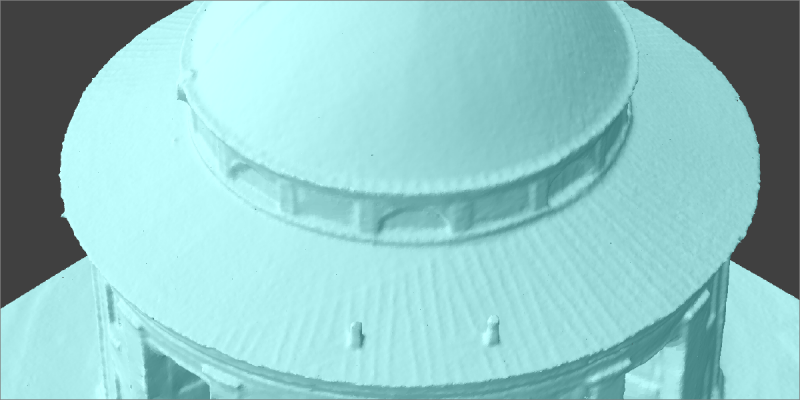
3D Mesh – a three-dimensional surface rendered from a dense point cloud or other input data. Also commonly referred to as a 3D Model.
Mesh Texture
Mesh Texture – raster data mapped on a 3D mesh surface. Textures make 3D mesh surfaces look realistic. Most common texture source data is the photos used in the photogrammetric reconstruction.
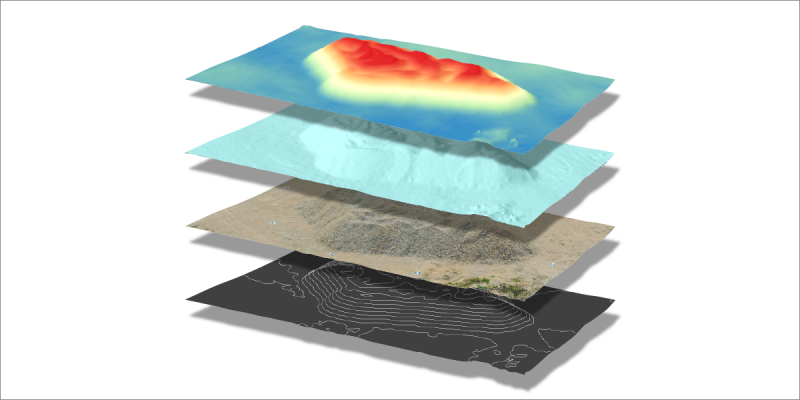
DEM
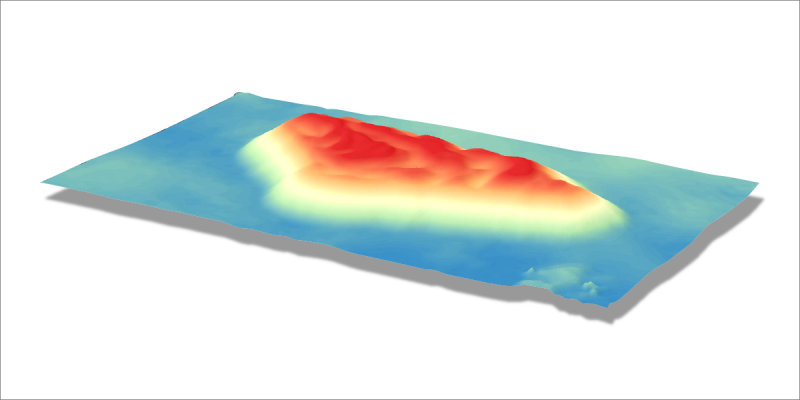
Digital Elevation Map – DEM – a raster or a 2.5D surface made from a 3D point cloud. Also known as a Heightmap. DEMs are raster images with each pixel value representing the height of the said pixel – not a color. Digital Elevation Map can be visualized in a 3D space and colored to make the height difference more distinguishable.
Orthophoto
Orthophoto also known as Orthorectified Imagery or Orthomosaic – a computed top-down photograph with corrected perspective. Orthophoto images are made for mapping and inspection and represent the scene as seen directly from above.
Contour Lines
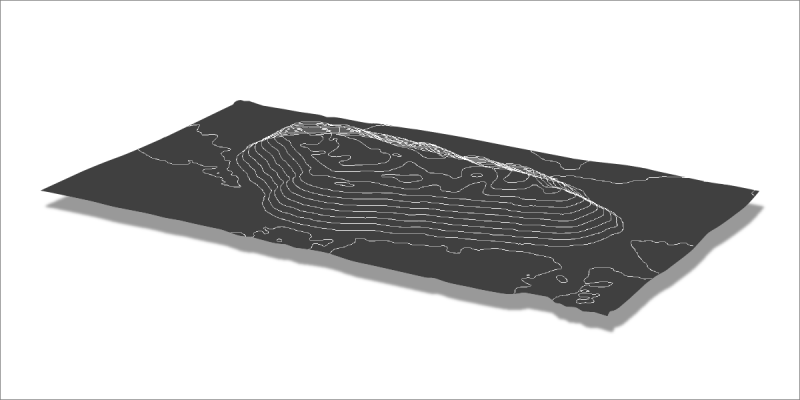
Contour Lines also known as Isohypses – represent the same height values on a surface. Contour lines can be created from height maps and are another way of describing the surface undulations.
Breaklines
Breaklines – lines that mark a sudden change in slope angle on a surface. Breaklines can be either generated from a surface or added to a surface to adjust and improve the said surface.
Referencing
Referencing – a system designed to add location and scale data to a photogrammetry project. Referencing systems can use various types of input data to move, scale, rotate, translate and warp point clouds and adjust camera positions. Referencing enables measurements and positioning of photogrammetry projects.
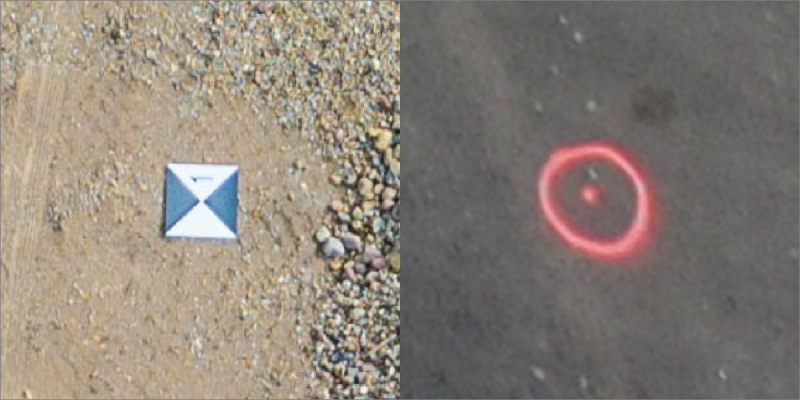
GCPs
Ground Control Points – GCPs – points on the scanned object or area used for referencing. These points must be visible and have their precise coordinates measured to work as GCPs.
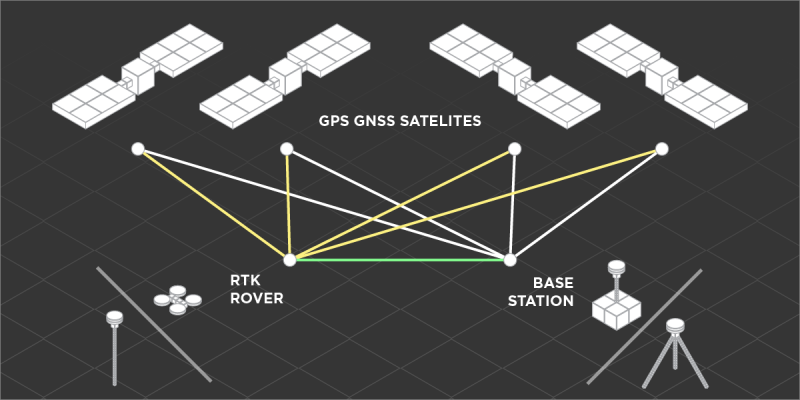
RTK
Real Time Kinematic– RTK – technology that allows GPS units to have precise location data. RTK works by correcting errors in satellite signals used for triangulation. RTK can be found in drones, survey equipment, farm equipment, military equipment, and other places where precise location data is needed.

Photographer - Drone Pilot - Photogrammetrist. Years of experience in gathering data for photogrammetry projects, client support and consultations, software testing, and working with development and marketing teams. Feel free to contact me via Pixpro Discord or email (l.zmejevskis@pix-pro.com) if you have any questions about our blog.
Related Blog Posts
Our Related Posts
All of our tools and technologies are designed, modified and updated keeping your needs in mind

Accuracy of Your Photogrammetry Project
Accuracy in photogrammetry is a multifaceted point of discussion. We can talk about absolute, relative, or even geometric accuracy, to name a few. No tool or technique can really prove anything beyond reproach.

Buying a Used Drone - Mavic 2 Pro in 2024
Buying used gear is an excellent way to save money and obtain something that may not be on sale anymore. With drones reaching the 4th or 5th technological generation, the used drone market is becoming more extensive.

Photogrammetry Processing - Common Hardware and Software Issues
Photogrammetry requires complex processing and data crunching to turn photos into 3D models. We need a powerful machine to run the software and all its processes. Not only that, but the software within our machine may impact the performance of photogrammetry software in various ways.
Ready to get started with your project?
You can choose from our three different plans or ask for a custom solution where you can process as many photos as you can!
Free 14-day trial. Cancel any time.
.svg@webp)