Glossary Part 3
 Lukas Zmejevskis
Lukas Zmejevskis

Welcome to the third part of our glossary, which covers most of the terminology used in our blog and in and around general photogrammetry-related conversations. As we make more of these terms, they get more technical and more challenging to explain in a few sentences. Still, we try to provide an easily understandable, short explanation as best we can. At the same time, you can find more technical and detailed breakdowns on sites like Wikipedia.
Glossary Part 1
Glossary Part 2
AI
AI - Artificial Intelligence - a broad term and a popular buzzword these days. Traditionally, genuine artificial intelligence means a fully self-aware and sentient machine capable of making intelligent decisions or even having feelings - a singularity. But in popular culture and day-to-day use, we refer to anything optimized, altered, or generated using complex algorithms with prior training or machine learning. As a term in human culture, AI will continue to evolve and change along with technology.

Machine Learning
Machine Learning - is also a broad term in computer science. Machine learning is essentially algorithms and programming rules that can further discover more algorithms and ways to solve specific issues or achieve goals themselves. At the same time, it would otherwise be impractical or even impossible for human programmers.
Machine Vision
Machine Vision - technology that allows a computer to see things in the real world. With digital cameras, machine vision is used to gather and analyze visual data for inspection, automatization, guidance, quality control, and many other purposes. Machine vision is essential in modern industrial processes. It is becoming more mainstream in household use, i.e., security systems, 3D printing, etc.
Procedural Generation
Procedural Generation - a process of creating data algorithmically, most commonly with the help of computer processing. Everyday use case examples are texture and landscape generation in video games, 3D scenes, or asset creation for movies. Procedural generation can create massive amounts of unique objects or patterns that follow specific rules.
Imaging Pipeline
Imaging Pipeline - image pipeline or video pipeline. A set of objects and actions needed to process and display a captured scene. An imaging pipeline is everything that helps to create, alter, and show a photo or a video for a person to see. For example, a digital imaging pipeline can be divided into camera components such as lens, sensor, buffer, and processor or digital algorithms like debayering and chroma subsampling.
Camera Intrinsics
Camera Intrinsics - unique values for a camera and lens combination, used in photogrammetry for 3D reconstruction. Every physical combination will have unique intrinsic values, which can be described with specific numbers. Camera intrinsics are essential for camera calibration and, therefore, accuracy in photogrammetric 3D models.
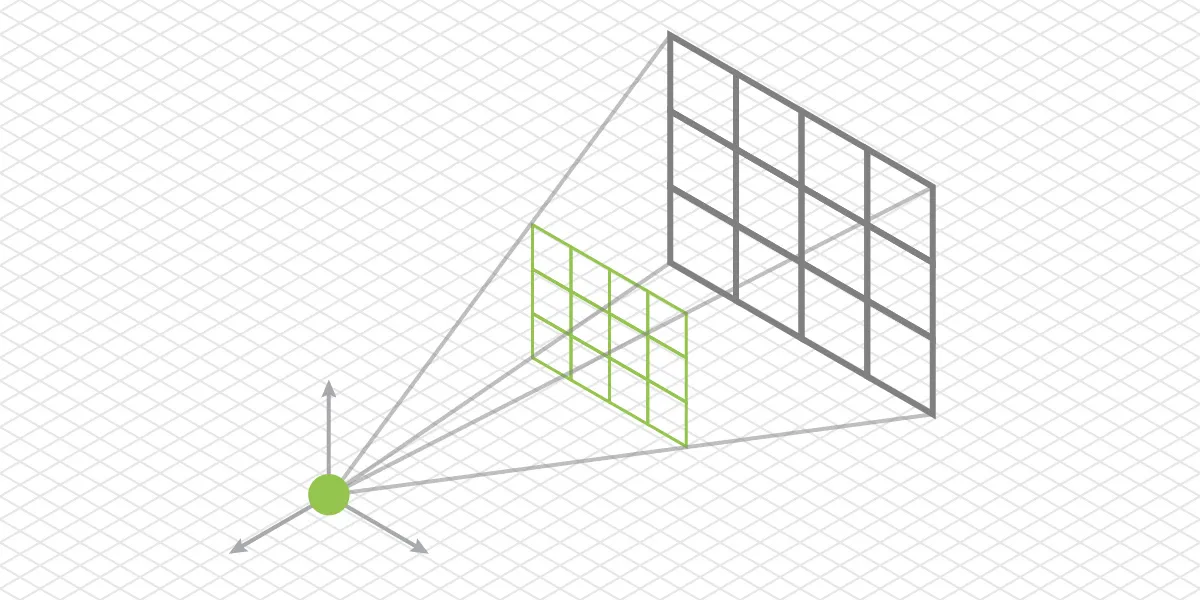
SFM
Structure from motion or SFM - a fundamental photogrammetry concept that allows estimating the 3D structure of a scene (and obtaining camera positions) from multiple 2D images that overlap the same scene. These 2D images must be made in different places to enable different perspectives of the same scene - the underlying concept of digital 3D photogrammetry.
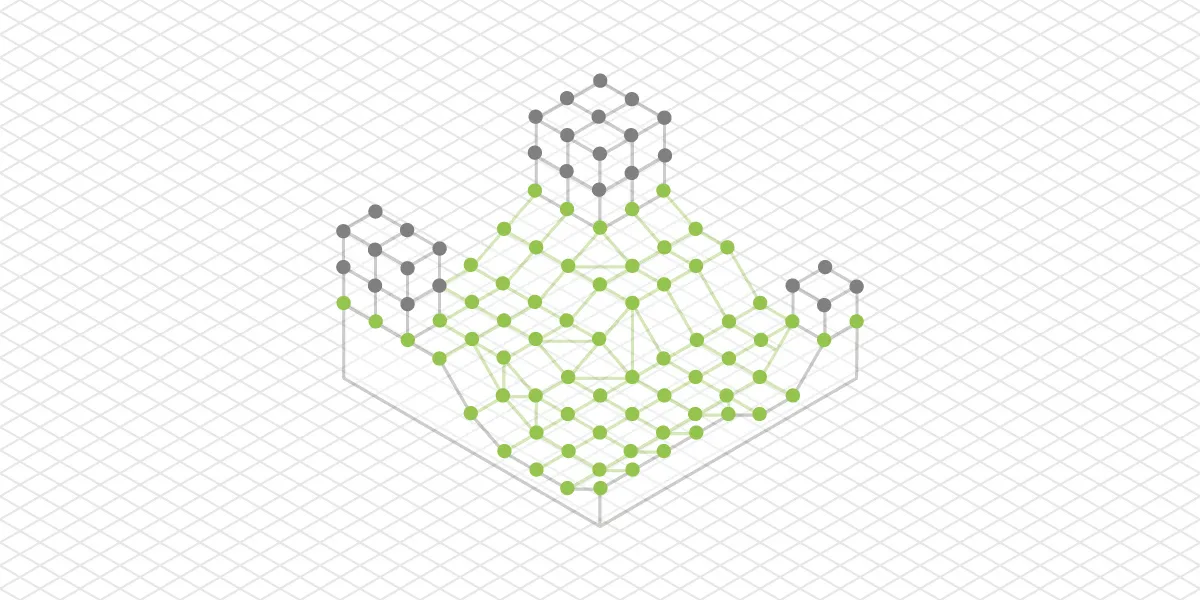
Point Cloud Classification
Point Cloud Classification - the process of sorting 3D point cloud points into categories such as ground, vegetation, roof, walls, etc. A classified point cloud allows for quickly removing particular objects from the 3D scene or doing other types of selective data analysis.
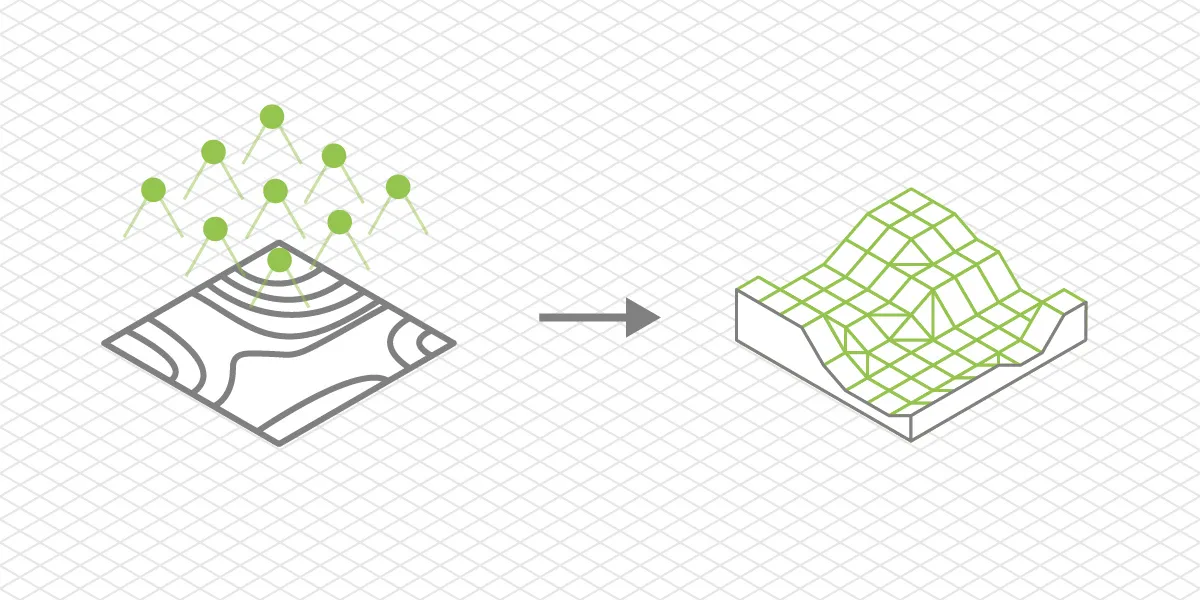
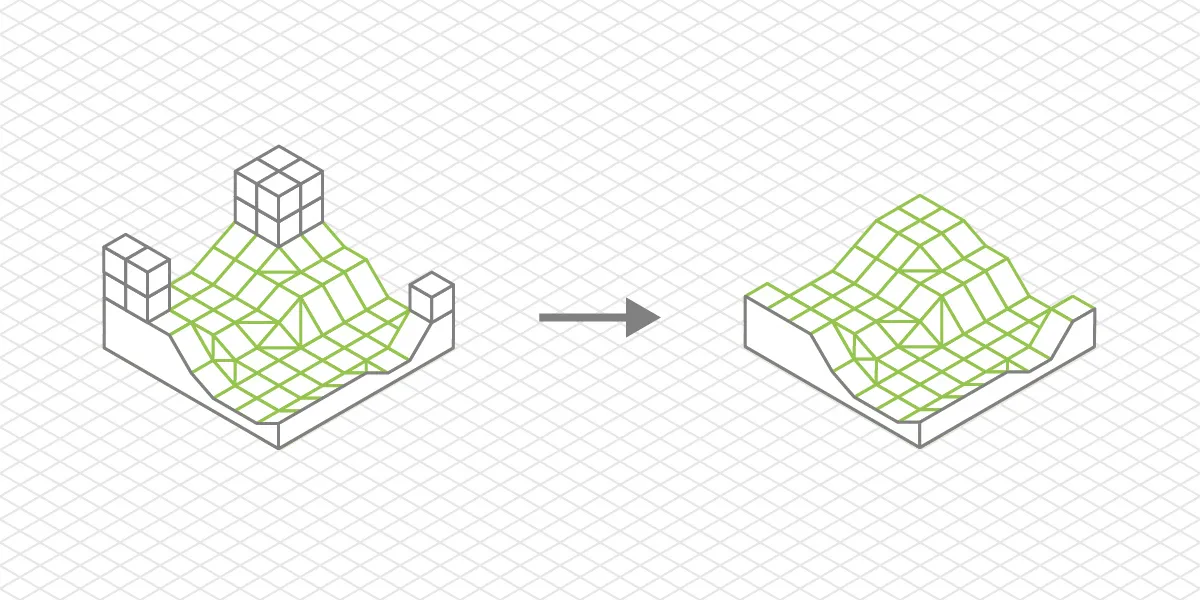
DTM
DTM or Digital Terrain Model - a digital 3D model or a 2.5D elevation map that only represents the bare earth surface data. Such models are created from classified point clouds where all other classes of points, such as vegetation or buildings, are removed.
UV Mapping
UV mapping - a process of projecting a 3D model to a 2D plane. This process is commonly used for texture mapping and is one of the fundamental processes in 3D modeling.
Texture Map
Texture Map - a 2D image or a set of images used for texturing a 3D model. It contains the visual information on a 2D image, which will be used on a 3D model to determine its complete appearance. Texture maps consist of many different types of maps, which can make the 3D model look photo-realistic or stylized according to needs.
Ray Tracing
Ray Tracing - is a computation technique used to calculate light transport in a 3D scene. Ray tracing attempts to simulate photons bouncing or refracting in a 3D space like in the real world. Applying ray tracing to a scene can make it look hyper-realistic and immersive. Real-time ray tracing is becoming more popular in games due to hardware acceleration, which makes it fast enough for real-time rendering.

Rasterization
Rasterization - a process of converting vector graphics into a raster - image made of pixels. Rasterization is the classic technique of rendering 3D models for screen display and is much faster than ray tracing. Rasterization techniques must be used with shaders to convey a complete image.
Map Projection
Map projection - a technique of representing a curved and uneven surface of our planet onto a flat 2D map. Showing a curved surface on a flat map without distortions is impossible. Hence, various projections always compromise in specific ways.
Lidar
LiDAR - Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging - a method and a technology of 3D scanning. Lidar sensors project lasers onto surfaces and measure the time reflected light returns to the sensor, thus determining the distance to the surface. Lidar can provide excellent accuracy point clouds for further data processing and analysis.
Spectral Imaging
Spectral Imaging - an imaging technique and technology in which a camera captures a specific wavelength or a range of wavelengths from the electromagnetic radiation spectrum beyond visible light. It is done to see beyond human vision by converting spectral imagery to visible light representation.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal Imaging - a subset of spectral imaging focusing on infrared radiation - heat. Thermal imagers are the most popular type of spectral camera, widely used in search and rescue and inspection fields.

GNSS
GNSS - global navigation satellite system - more commonly and strictly inaccurately referred to as GPS. GPS technically is a name (global positioning system), a single system of USA origin, while the entire planet's GNSS contains GPS, Beidou, GLONASS, and GALILEO systems.

Fisheye Lens
Fisheye lens - an ultra-wide angle lens that projects a distorted image onto the imaging sensor or film. Fisheye lenses offer the widest possible field of view at the cost of losing natural undistorted perspective.

Rectilinear Lens
Rectilinear lens - a traditional type of lens that produces straight perspective lines. It does not mean that all rectilinear lenses have zero distortion. For example, making an ultrawide rectilinear lens without distortion is extremely difficult. Only the best lenses on the market display anything close to zero geometric distortion. Rectilinear only means that the image projection type represents a natural perspective, unlike the fisheye lens.
360 Camera
360 Camera - a camera that captures a full 360 view around it. Most 360 cameras have two extremely wide-angle fisheye lenses in front of identical sensors and stitch the final image from the two combinations into a single 360 photo.

Waypoints
Waypoints - points with location data on a map. It is most commonly used in the context of UAV flight planning. These waypoints are points in space that the drone must fly through to achieve a preprogrammed mission.

Telemetry
Telemetry - a broad term encompassing any data used for real-time monitoring or logging. Usually, telemetry is used to monitor how a complex device with many moving parts works. Telemetry data results from various sensors reporting values from which conclusions about the device's current state can be made.
Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing - a science of acquiring data from an object or environment by measuring its electromagnetic radiation without physical contact or sample extraction. Remote sensing usually refers to satellite aircraft or UAV-acquired data. Remote sensing can be passive or active. Passive means measuring naturally reflected or emitted electromagnetic radiation, while active means observing the reflection of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the remote sensing device, for example - Lidar.
Geospatial Data
Geospatial Data or Geodata - any data that includes its location in the real world. Any type that can be classified as geospatial if it meets this principle requirement.


Photographer - Drone Pilot - Photogrammetrist. Years of experience in gathering data for photogrammetry projects, client support and consultations, software testing, and working with development and marketing teams. Feel free to contact me via Pixpro Discord or email (l.zmejevskis@pix-pro.com) if you have any questions about our blog.
Related Blog Posts
Our Related Posts
All of our tools and technologies are designed, modified and updated keeping your needs in mind
Photogrammetry 202 - Pixpro Blog Index
In our final blog post of the year, we are indexing Pixpro photogrammetry blog posts from the last two years. After publishing regularly for a while, things tend to scatter: posts about workflows, Pixpro features, hardware tests, random experiments, use cases, comparisons.
Travel Photogrammetry - More Fun than 2D Photos
Sometimes a 2D photo does not do justice to a moment or a place, and you wish you had something more… dimensional. Something that captures shape, texture, and the little details that flat images tend to flatten even more.
Budget in Photogrammetry - Affordable to Medium to Premium
Photogrammetry, like many other professions, hobbies, or disciplines, can have different budget tiers. In this article, I will provide my opinion on what I consider to be photogrammetry gear, ranging from affordable to premium to high-end tiers.
Ready to get started with your project?
You can choose from our three different plans or ask for a custom solution where you can process as many photos as you like!
Free 14-day trial. Cancel any time.
Welcome to Pixpro
Sign in
And access your account.
.svg@webp)